In the previous article ,we talked about the two network
models which we consider, whenever we
talks about computer networking, for effective communication between the
network. The two network models are OSI and TCP/IP network models.
These models are used to connect the sender with the receiver in a network.
These are the layered network models in which the data has to pass through
different layers of these models on both sides of the sender and the receiver.
Today, we will talk
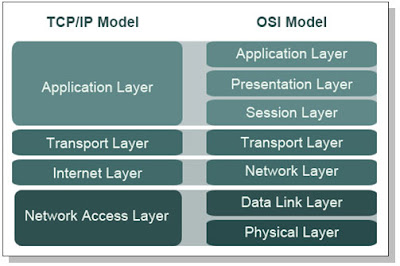
about the working of each layer of the OSI model. As we know that OSI model is
a
7 layer network model and the TCP/IP is a 4 layer network model. OSI model is
a reference model whereas TCP/IP model
is its implementation.
So we will just talk about the working of the
OSI network model from where the working of the 4 layers of the TCP/IP model
can be understood easily.
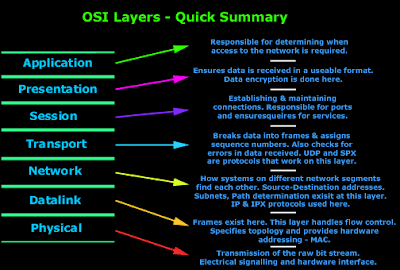
Different layers of OSI model:- The different layers of OSI
network model are :-
1. Application Layer
2. Presentation Layer
3. Session Layer
4. Transport Layer
5. Network Layer
6. Data Link Layer
7. Physical Layer
Let’s talk about the function of each layer one by one.
1) Application Layer:-
The application layer is the closest layer of the OSI model to the user
which means that both the OSI application layer and the user can interact
directly with the software application. This layer is responsible to provide
services to the user. It serves as the window for users to access the network
services. The data provided by the user is then forwarded to the next layer,
Presentation layer. The example of the application layer is a browser like
google chrome, mozilla firefox etc.
2) Presentation Layer:-
This layer adds its own protocols in the form of header to the data
received from the application layer. Presentation layer is responsible for the
translation, Encryption (to encrypt the data for security purposes) of data,
Decryption ( to decrypt the encrypted data) of data, Compressing( to reduce the
no. of bits) . So, to convert the data to the format required by the sender or
the receiver, to provide the privacy by encryption and to compress the data is
the main task of this layer. The data from presentation layer is then
transmitted to the next layer, Session layer.
3) Session Layer:- This layer adds its own protocols ,in the
form of header, to the data received from the Presentation Layer. This layer is
for the session establishment, maintainence and termination of the session.
Session layer is responsible for the dialog control and synchronization. In
dialog control, this layer allows the communication either in Half-Duplex or in
Full-Duplex mode. It also adds the checkpoints to the stream of data. The data
of the session layer is then moved to the next layer, Transport layer.
4) Transport Layer:- The transport layer adds its own protocols
in the form of headers to the data received from the session layer. Transport
Layer is responsible for the segmentation of the data, arrange them in sequence
with no loss and duplication and provide the acknowledgement of the successful
data transmission. It only sends the next data if no error occurred in the
previous data transmission. The message is divided into segments, each segments
having sequence number which helps to reassemble the message correctly in the
receiver side. The data of transport layer is transmitted to the next layer,
Network layer.
5) Network Layer:- This layer adds its own protocols in the
form of headers to the message received from the transport layer. The header of
the network layer consists of the logical address of the sender and the
receiver. Logical address is different from the MAC address (physical address).
Logical address is the address given to each computer on a network for the
complete transmission of the message from the sender to its receiver. Network
layer is required where the two systems are connected to different networks
having connecting devices between them. The data from the Network layer then
sends to the next layer called Data Link Layer.
6) Data Link Layer:- This layer adds its own protocols in the
form of headers to the data received from the network layer. Data link layer is
responsible for the speed, security, physical addressing, error free
transmission of data frames from one node to another node over the physical
layer, framing etc. Data link layer divides the message into manageable data
units called frames. This layer adds the header to each frames to define the
sender and the receiver over a network. Data from the data link layer is
transferred to the next layer called Physical Layer.
7) Physical Layer:- This layer is the costliest layer of all.
The purpose of this layer is to carry the data from the sender to the receiver.
Physical layer can be a wired media (guided media) or wireless media (unguided
media).In a wired media, physical layer can be twisted pair cables, coaxial
cable or optical fibres. It can be of different network topologies like Mesh
topology, Bus topology, Star topology and Ring topology. In a wireless media,
physical layers can be radio waves or microwaves. The physical layer is
responsible for the transmission of bits from one node to the next node.
Credits:- Yuvraj Salaria